What is Bitcoin Mining and How Does it Work?
Bitcoin mining seems confusing.
Computers mining for virtual coins? Is Bitcoin mining just free money?
Well, it’s much more than that!
If you want the full explanation on Bitcoin mining, keep reading…
Chapters
Chapter 1
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network.
Miners provide security and confirm Bitcoin transactions.
Without Bitcoin miners, the network would be attacked and dysfunctional.
Bitcoin mining is done by specialized computers.
The role of miners is to secure the network and to process every Bitcoin transaction.
Miners achieve this by solving a computational problem which allows them to chain together blocks of transactions (hence Bitcoin’s famous “blockchain”).
For this service, miners are rewarded with newly-created Bitcoins and transaction fees.
Chapter 2
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
What is Bitcoin mining actually doing?
Miners are securing the network and confirming Bitcoin transactions.
Miners are paid rewards for their service every 10 minutes in the form of new bitcoins.
What is Bitcoin Mining Actually Doing?
What is the point of Bitcoin mining? This is something we’re asked everyday!
There are many aspects and functions of Bitcoin mining and we’ll go over them here. They are:
- Issuance of new bitcoins
- Confirming transactions
- Security
Mining Is Used to Issue new Bitcoins
Traditional currencies–like the dollar or euro–are issued by central banks. The central bank can issue new units of money at any time based on what they think will improve the economy.
Bitcoin is different.
With Bitcoin, miners are rewarded new bitcoins every 10 minutes.
The issuance rate is set in the code, so miners cannot cheat the system or create bitcoins out of thin air. They have to use their computing power to generate the new bitcoins.
Miners Confirm Transactions
Miners include transactions sent on the Bitcoin network in their blocks.
A transaction can only be considered secure and complete once it is included in a block.
Why?
Because only a when a transaction has been included in a block is it officially embedded into Bitcoin’s blockchain.
More confirmations are better for larger payments. Here is a visual so you have a better idea:
Why Does Bitcoin Need Miners?
In short, miners secure the Bitcoin network.
They do this by making it difficult to attack, alter or stop the network.
The more miners that mine, the more secure the network.
The only way to reverse Bitcoin transactions is to have more than 51% of the network hash power. Distributed hash power spread among many different miners keeps Bitcoin secure and safe.
Chapter 3
How to Mine Bitcoins
Actually want to try mining bitcoins?
Well, you can do it. However, it’s not profitable for most people as mining is a highly specialized industry.
Most Bitcoin mining is done in large warehouses where there is cheap electricity.
To be real:
Most people should NOT mine bitcoins today.
Most Bitcoin mining is specialized and the warehouses look something like this:
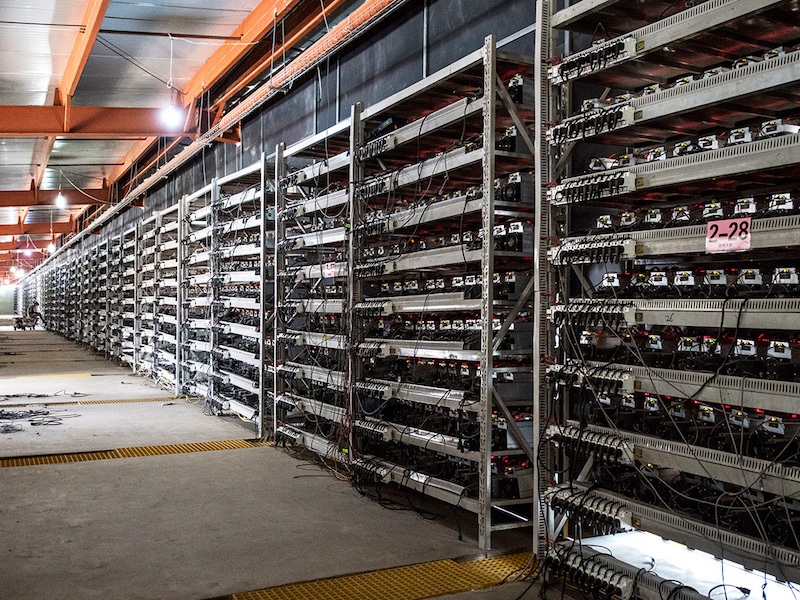

That’s who you’re up against! It’s simply too expensive and you are unlikely to turn a profit.
However:
For hobby mining, we’ll show you some steps you can take to get started mining bitcoins right now.
Step #1: Get Bitcoin Wallet
When earning bitcoins from mining, they go directly into a Bitcoin wallet.
You can’t mine without a wallet.
If you aren’t sure which one to buy, our best bitcoin wallets guide will help you select a wallet.
Step #2: Find a Bitcoin Exchange
When earning bitcoins from mining, you may need to sell the coins to pay for power costs. You may also need to buy coins on exchanges.
Step #3: Get Bitcoin Mining Hardware
You won’t be able to mine without an ASIC miner.
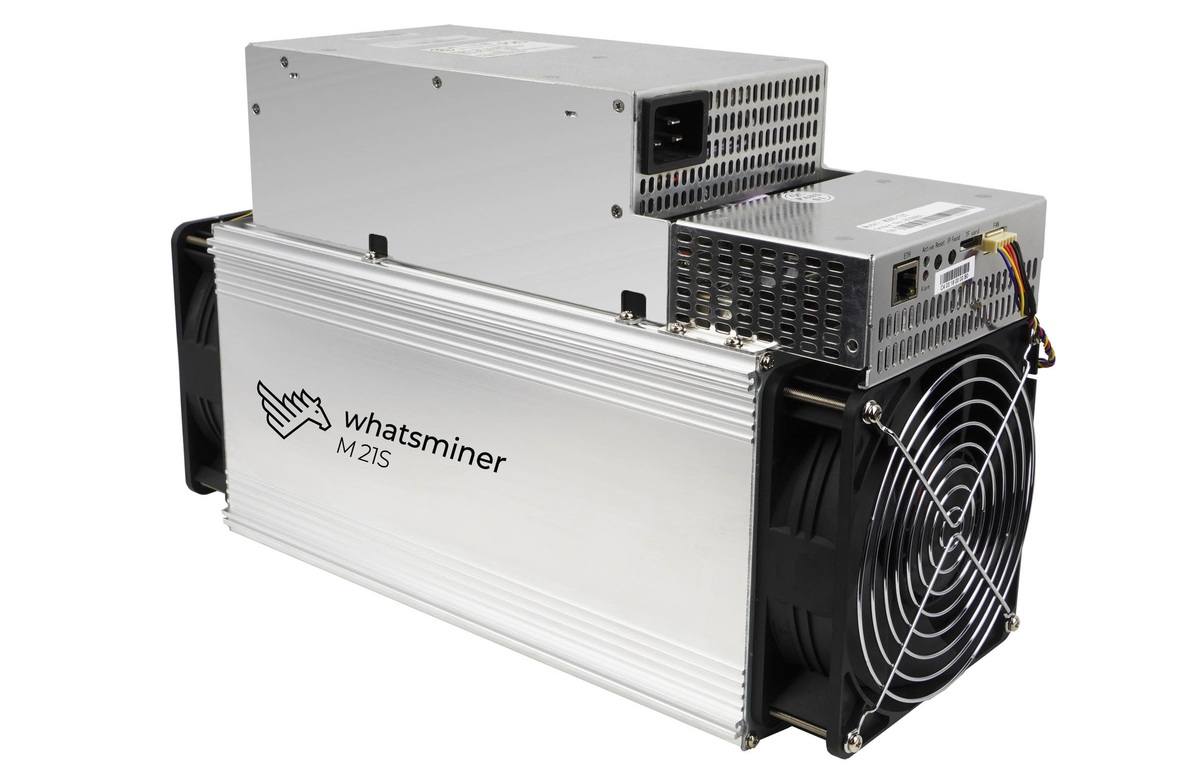

Don’t even try mining bitcoins on your home desktop or laptop computer! You will earn less than one penny per year and will waste money on electricity.
Step #4: Select a Mining Pool
Once you get your mining hardware, you need to select a mining pool.
We recommend Slush Pool, as it is the oldest and has the best User Interface to make it easy to use. Check it out:
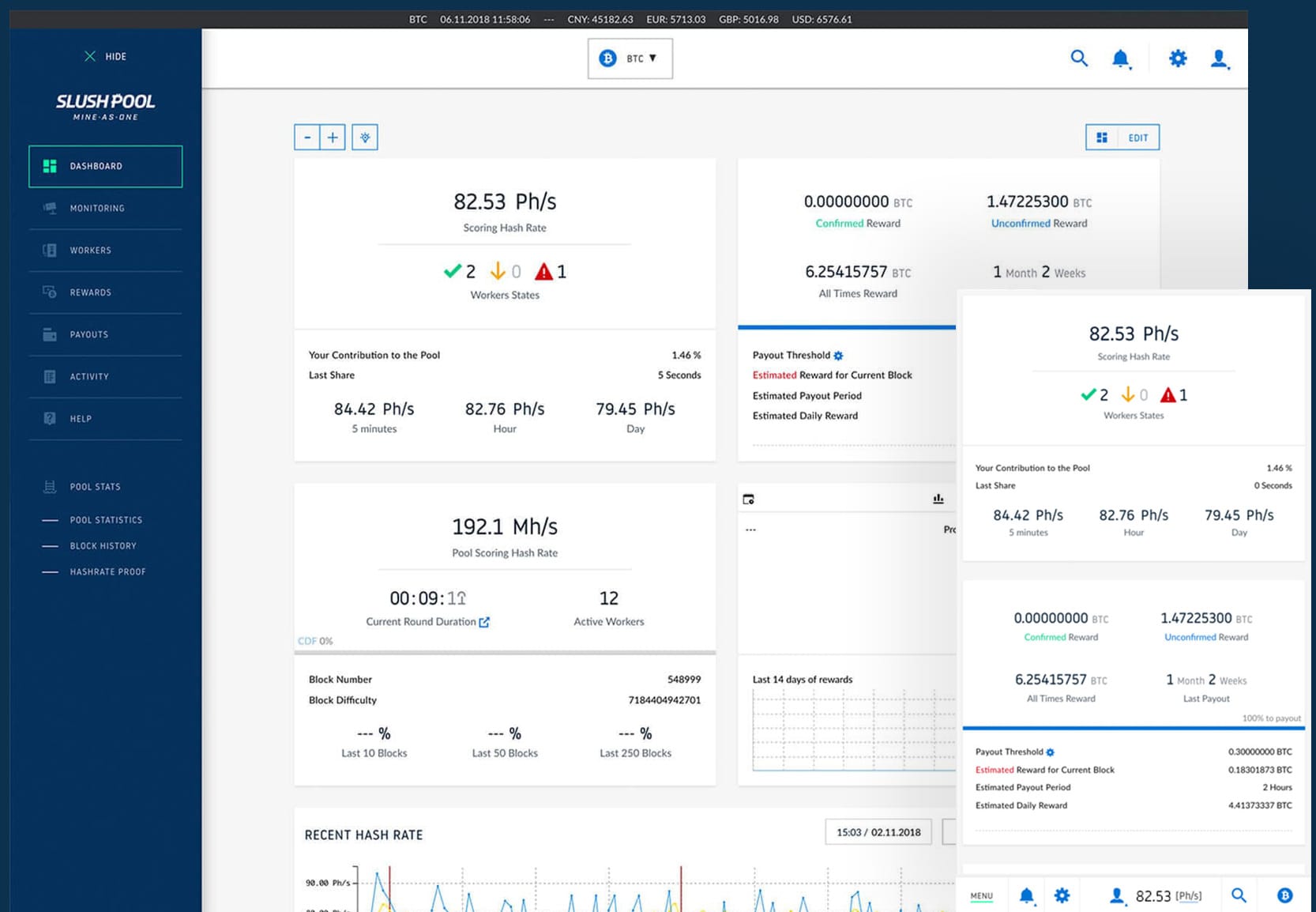
Without a mining pool, you would only receive a mining payout if you found a block on your own. This is called solo mining.
We don’t recommend this because your hardware’s hash rate is very unlikely to be anywhere near enough to find a block solo mining.
How do mining pools help?
By joining a mining pool you share your hash rate with the pool. Once the pool finds a block you get a payout based on the percent of hash rate contributed to the pool.
If you contributed 1% of the pools hashrate, you’d get .125 bitcoins out of the current 12.5 bitcoin block reward.
Step #5: Get Bitcoin Mining Software
Bitcoin mining software is how you actually hook your mining hardware into your desired mining pool.
You need to use the software to point your hash rate at the pool.
Also in the software you tell the pool which Bitcoin address payouts should be sent to.
If you don’t have a Bitcoin wallet or address learn how to get one here.
There is mining software available for Mac, Windows, and Linux.
Step #6: Is Bitcoin Mining Legal in your Country? Make Sure!
This won’t be much of an issue in MOST countries.
Consult local counsel for further assistance in determining whether Bitcoin mining is legal and the tax implications of doing the activity.
Like other business, you can usually write off your expenses that made your operation profitable, like electricity and hardware costs.
Step #7: Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable for You?
Do you understand what you need to do to start?
You should run some calculations and see if Bitcoin mining will actually be profitable for you.
You can use a Bitcoin mining calculator to get a rough idea.

Our mining profitability calculator will help you figure out if mining will be worth it
I say rough idea because many factors related to your mining profitability are constantly changing.
A doubling in the Bitcoin price could increase your profits by two.
But:
It could also make mining that much more competitive so your profits remain the same.
Learn how to Mine Bitcoins on Android or iOS.
Here’s what’s funny:
You actually CAN mine bitcoins on any Android device.
Using mining software for Android you can mine bitcoins or any other coin.
What’s not so fun?
You’ll likely make less than one penny PER YEAR!
Why?
Android phones simply are not powerful enough to match the mining hardware used by serious operations.
So, it might be cool to setup a miner on your Android phone to see how it works. But don’t expect to make any money.
Do expect to waste a lot of your phone’s battery!
Chapter 4
What is Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Bitcoin mining hardware (ASICs) are high specialized computers used to mine bitcoins.
The ASIC industry has become complex and competitive.
Mining hardware is now only located where there is cheap electricity.
When Satoshi released Bitcoin, he intended it to be mined on computer CPUs.
However:
Enterprising coders soon discovered they could get more hashing power from graphic cards and wrote mining software to allow this.
GPU Mining
GPU mining is when you mine for Bitcoins (or any cryptocurrency) using a graphics card.
If you were to open your desktop computer right now, you’d likely see a piece of hardware that looks like the one below:
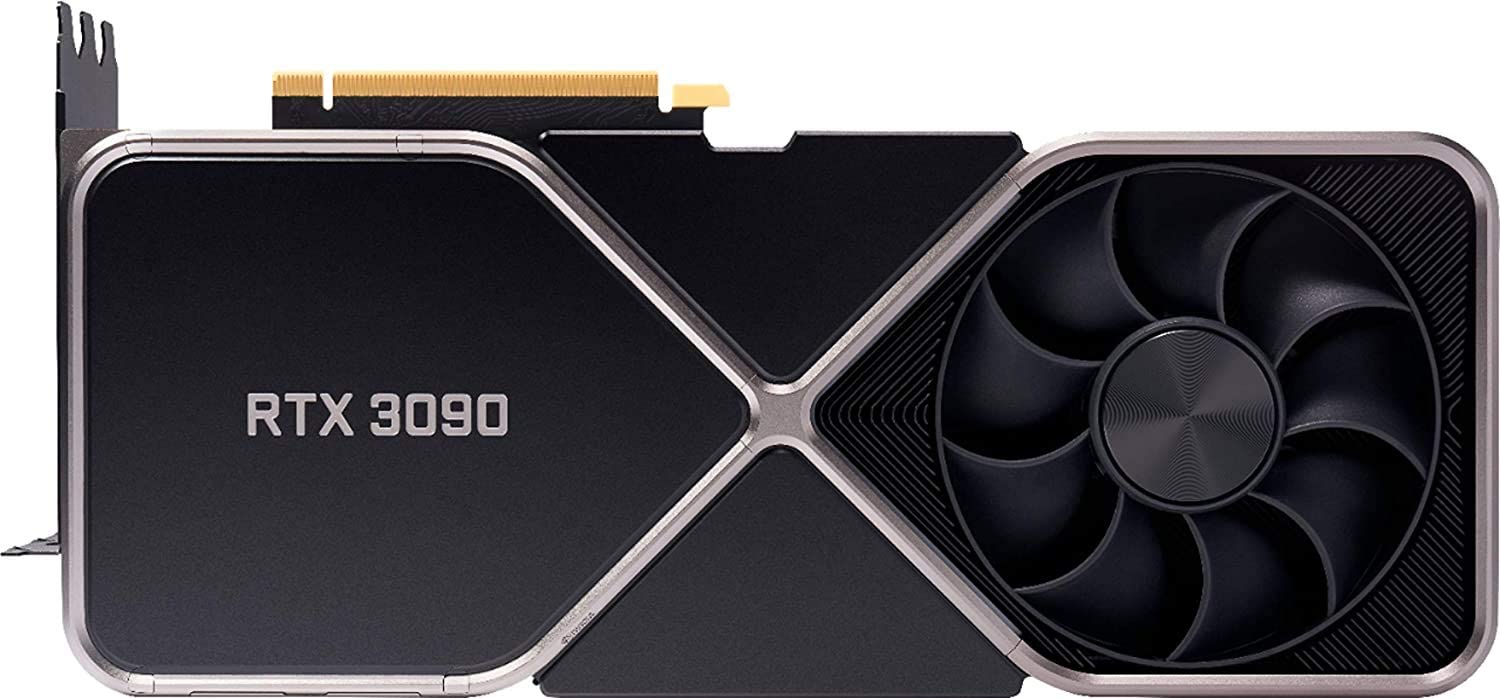

GPU mining was one of the earliest forms of mining, but is no longer profitable due to the introduction of ASIC miners.
GPUs were surpassed in turn by ASICs(2).
ASIC Miner
ASIC stands for “Application Specific Integrated Circuit”. In plain English, that just means it is a chip designed to do one very specific kind of calculation. In the case of a Bitcoin ASIC miner, the chip in the miner is designed to solve problems using the SHA256 hashing algorithm.
Here is what an ASIC looks like:
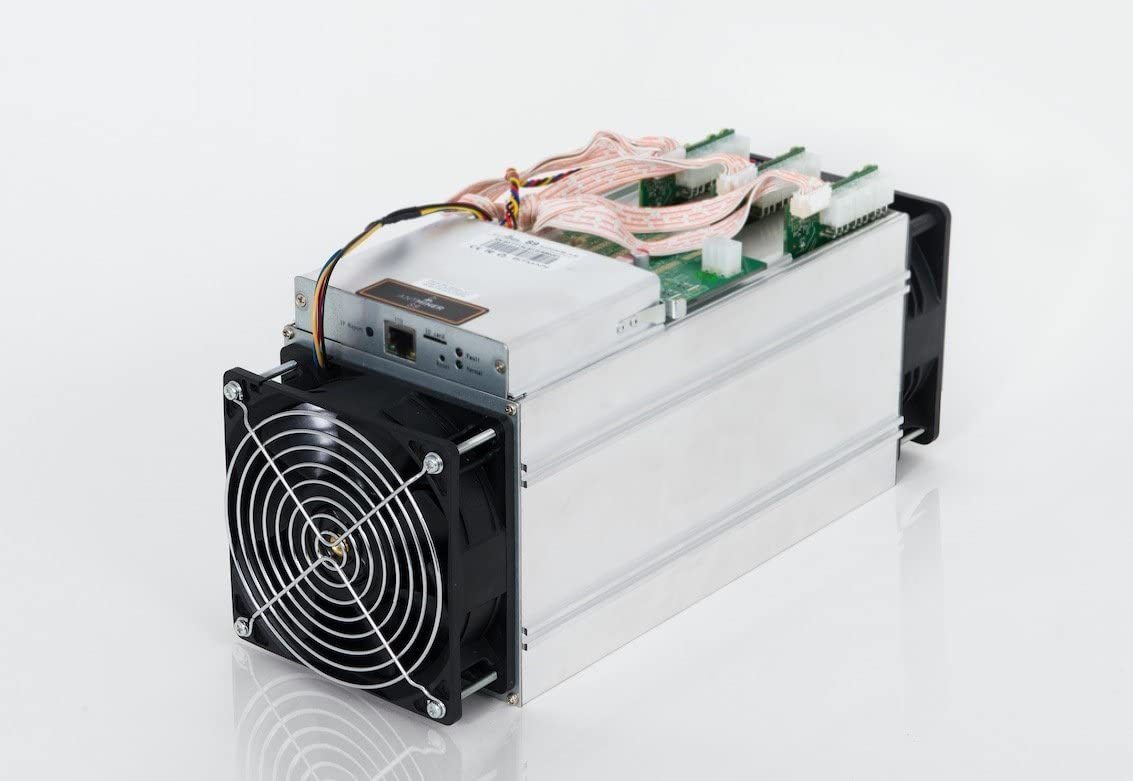

You can learn more about ASIC Miners on our mining hardware page].
Nowadays all serious Bitcoin mining is performed on ASICs, usually in thermally-regulated data-centers with access to low-cost electricity.
Economies of scale have thus led to the concentration of mining power into fewer hands than originally intended.
Chapter 5
What Are Bitcoin Mining Pools?
Mining pools allow small miners to receive more frequent mining payouts.
By joining with other miners in a group, a pool allows miners to find blocks more frequently.
But, there are some problems with mining pools as we’ll discuss.
As with GPU and ASIC mining, Satoshi apparently failed to anticipate the emergence of mining pools.
Pools are groups of cooperating miners who agree to share block rewards in proportion to their contributed mining power.
The pie chart below displays the current distribution of total mining power by pools:
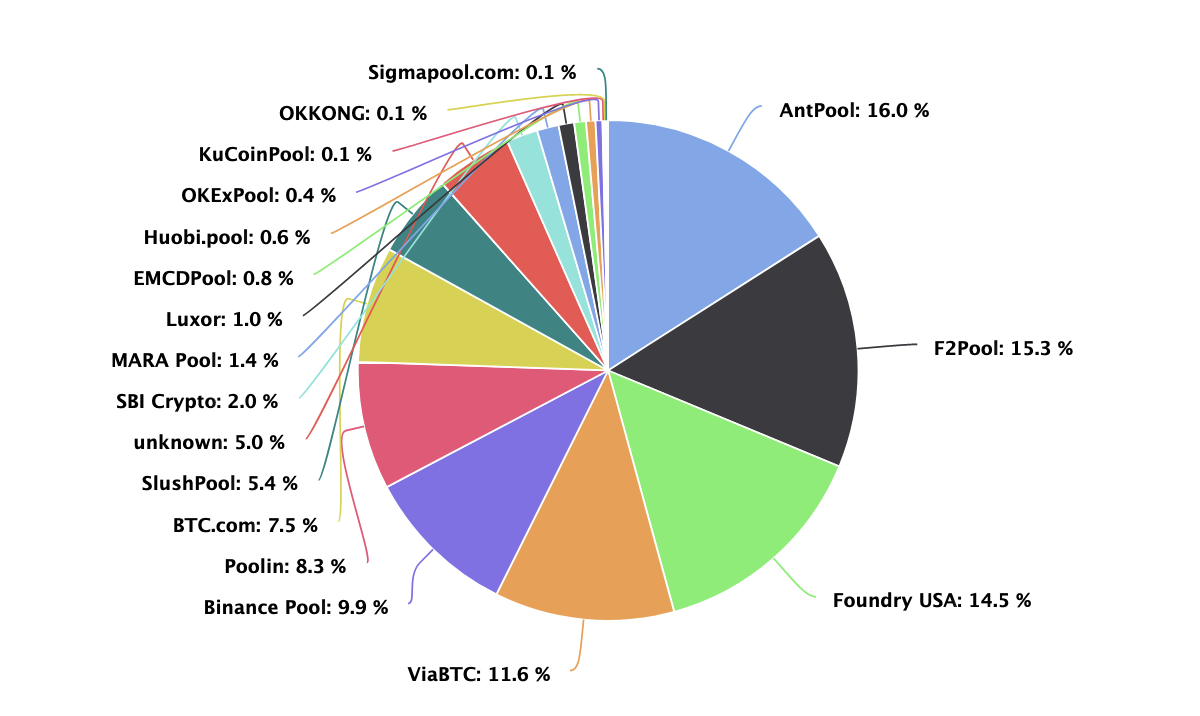
While pools are desirable to the average miner as they smooth out rewards and make them more predictable, they unfortunately concentrate power to the mining pool’s owner.
Chapter 6
The mining industry has come a long way since the early days of graphics card mining.
Today there are very professional industrial mining operations. Let’s take a look at how they work.
What does a mining farm look like?
Let’s take a look inside a real Bitcoin mining farm in Washington state.
Mining farms look very similar to a data center. They contain rows of hardware with powerful fans to keep the miners from over heating.
Mining farms are typically very industrial looking - they aren’t flashy or sleek. Usually, its just a warehouse with great temperature control.
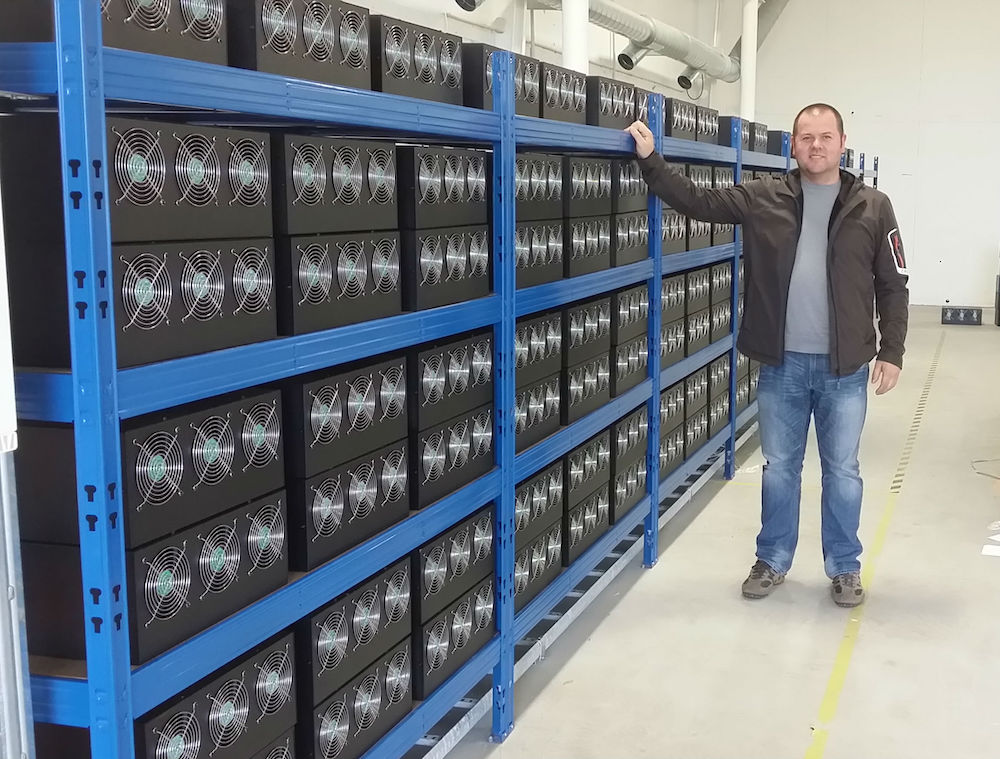

Bitcoin mining farms exclusively use ASIC miners to mine various coins. Many of these farms are minting several Bitcoins per day.
How much do crypto mining farms make?
How much a mining farm makes depends on many factors:
- The price it pays for electricity
- How old its mining hardware is
- The scale of its operation
- The price of Bitcoin when the miner sells it
- The level of difficulty when the Bitcoin is mined
By far, the biggest factor affecting how much money a mining farm makes is how much it pays for electricity. Nearly all mining farms are using the same hardware.
Since the reward for finding a block is fixed, and the difficulty is adjusted based on total processing power working on finding blocks at any given time, then electricity is the only cost that is variable. If you can find cheaper power than other miners, you can afford to either increase the size of your mining operation, or spend less on your mining for the same output.
How much electricity do mining farms use?
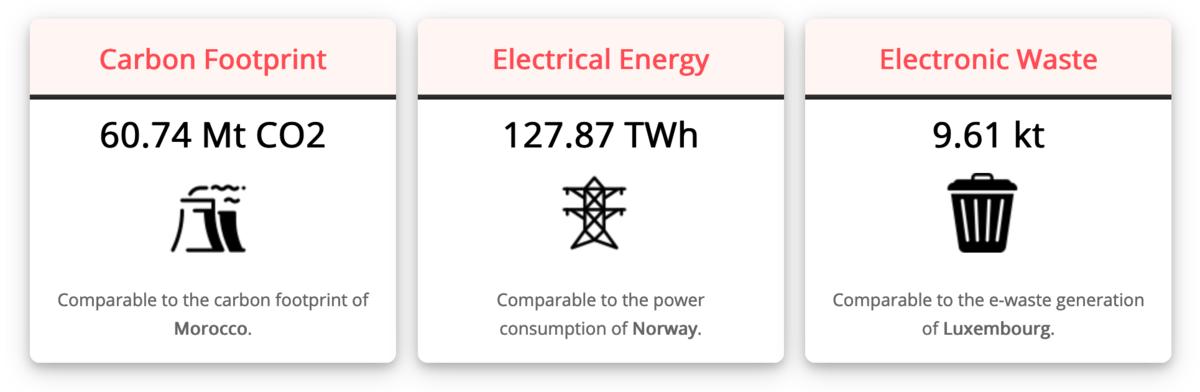
As previously mentioned, mining farms use a lot of electricity. How much they consume depends on how big their operation is. However the latest Bitmain ASIC miner consumes about 1350 watts.
In total, it is estimated that all mining farms will use about 127 Terawatt hours of electricity in the year 2021. That is roughly the equivalent to the yearly energy consumption of Norway.
Where are mining farms located?
Mining farms are located all over the world. We don’t know where every mining farm in the world is, but we have some educated guesses.
Most of the mining has been and still is located in China.
Why is so much Mining happening in China? Samson Mow of Blockstream and former CTO of BTCC mining pool explains.
The main advantages of mining in China are faster setup times and lower initial CapEx which, along with closer proximity to where ASICs are assembled, have driven industry growth there
 Samson Mow CSO, Blockstream
Samson Mow CSO, BlockstreamBonus Chapter 1
Colocation Mining

In this bonus chapter, we will learn about colocation bitcoin mining and its differences from cloud mining.
If you were interested in cloud mining, but are worried about falling victim to a scam, then this is the closest thing to it.
What is Colocation Mining?
Colocation mining is a business arrangement between a bitcoin mining management company and a customer.
The management company establishes a location to mine the bitcoins at and strikes a deal with a power company to get favorable prices on electricity.
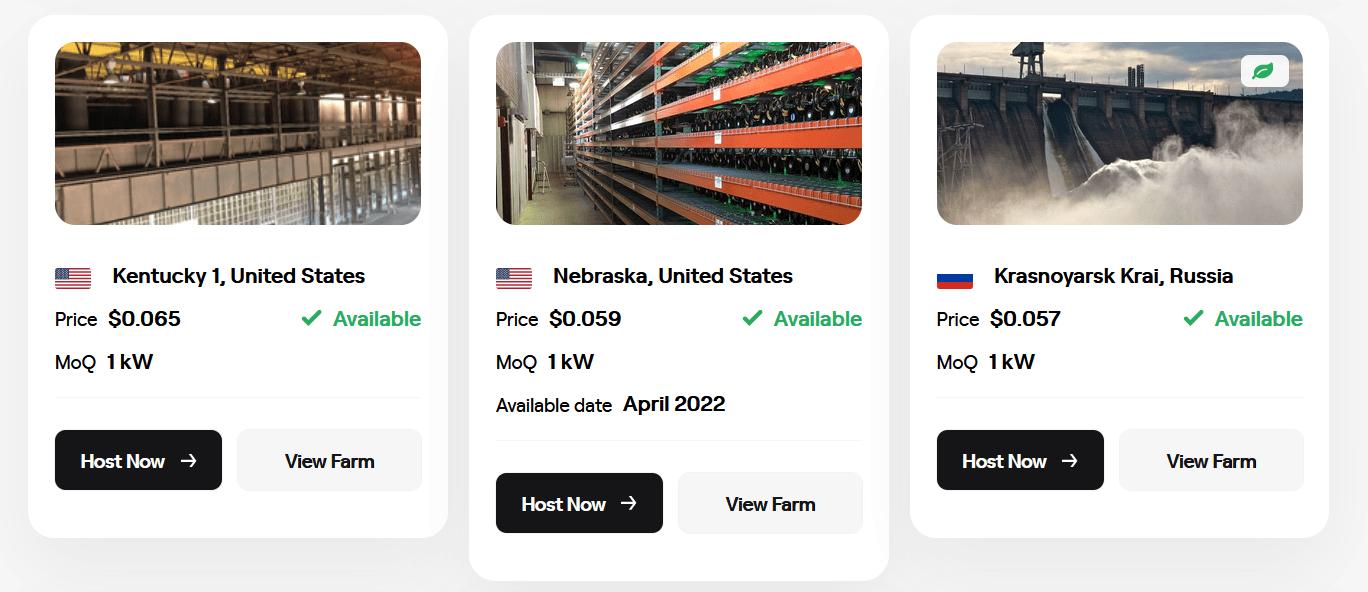
Compass Mining, a colocation company, offers many options on where you can host your miners.
The management company also has relationships with ASIC producers in order to get favorable prices on mining ASICs.
Finally, the management company employs workers to make sure the ASICs run smoothly while keeping the location safe from thieves.
Something very unique about colocation miners is that the management company may not own any of the ASICs itself.
Who owns the miners?
Well, you, the customer, do.
You contact the management company running the colocation mine, and purchase ASICs through them. The management company acts as a kind of ASIC broker.
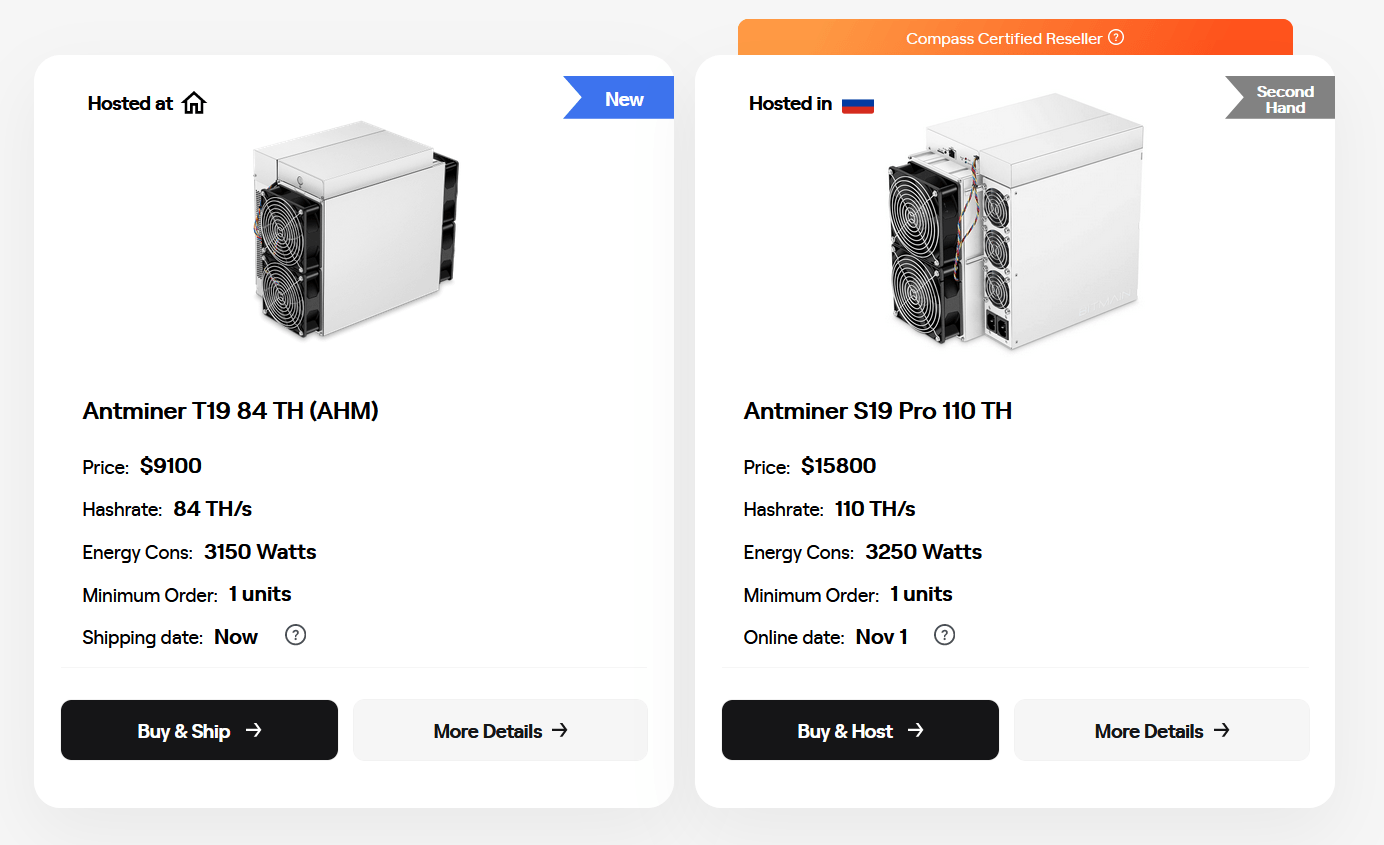
The hardware purchase page on Compass Mining’s Website
Once you have purchased your ASICs, the management company receives them at their mining location and installs them for you
How Does the Colocation Company Make Money?
The colocation management company makes money in several ways. Each management company is different, but they all make money using one or more of the following ways:
- They charge you a monthly hosting fee for maintaining the miners and keeping them safe in their mine.
- They make a commission for arranging the sale of the ASICs to you.
- They take a cut of the mining profits from all the miners in the mine.
- They add a surcharge onto the electricity that your ASICs consume in their mine.
- ASIC repair services in case your miners ever needs to be repaired.
So to summarize: in a colocation mining operation, you own, control, and monitor your own ASICs. The colocation mine custodies them and lets you know if there are any issues with them. They also keep them safe by securing and maintaining the mining site.
So now you may be wondering, how is this different from cloud mining?
First, we need to define what Cloud Mining is.
What is Cloud Mining?
Cloud mining is a business arrangement where a miner owns all of the ASICs in his mine.
He offers to sell some of his hashing power to you, the customer and you get any bitcoin mined using that hashing power.
In a cloud mining arrangement, you do not own anything.
You are effectively renting the hashing power from the miner in exchange for potential profits in bitcoin.
The Big Problem with Cloud Mining
There’s just one problem with this arrangement.
Since you do not own the ASICs, you have no control over what they mine, when they mine, how they mine, etc.
And because of this, cloud mining attracts lots of scammers.
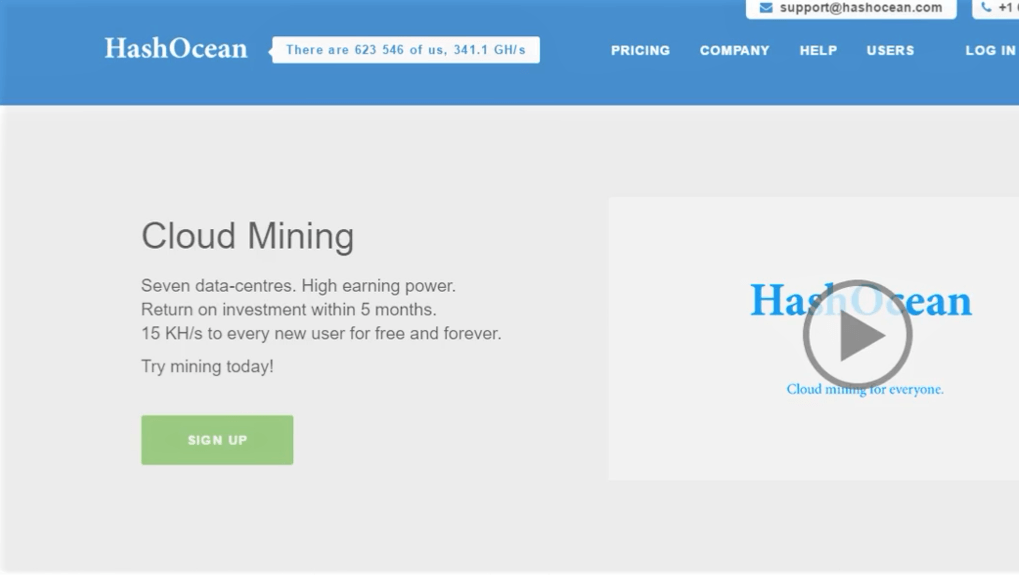
An old screenshot of Hash Ocean’s website promising free bitcoin rewards for life for early sign ups. They ended up being a scam.
In most cases, in a cloud mining operation…there are no miners.
They don’t exist. At all.
The only reason you ever make money is because someone else signed up and paid the cloud miner money to get started.
which means that cloud mining operations are almost always ponzi scams. New customers pay off the old ones until there are no new people to sign up.
At that point, the founders run away with as much money as they can.

Mining City, another famous cloud miner, was running a ponzi scheme where the founders ran away with the money.
And since no one actually owns any ASICs (including the cloud miner himself), there are no assets to liquidate to pay back the victims.
It’s all fictitious.
How is Colocation Mining different from Cloud Mining?
Aside from the fact that one of these models is typically legitimate and the other is typically a scam, there are some other differences even if you assume the cloud miner is running an honest operation.
First, in colocation mining, you own the ASICs. In cloud mining, you don’t.
Second, because you own the ASICs in colocation mining, you get to decide which coins you want to mine and how you want to mine them. In cloud mining, you just pay money to a miner and hope you get more back than you put in. It’s up to him to decide how and what to mine.
Is Colocation Mining a Good Alternative to Cloud Mining
If you want to mine, but don’t think you have enough money or experience to start your own mining farm, then colocation can be a great way to start mining.
It allows you to leverage the bargaining power on electricity and ASICs of a big mining operation without having to put up millions of dollars to start mining. In exchange for this, you pay a small fee and don’t need lots of expertise to get going.
Bonus Chapter 2
Important Bitcoin Mining Terms
In this bonus chapter, we will learn about some of the most common terms associated with bitcoin mining.
If you are thinking about mining at any level, understanding what these terms means will be crucial for you to get started.
Miner
Anyone who mines Bitcoins (or any other cryptocurrency).
Block Reward
The block reward is a fixed amount of Bitcoins that get rewarded to the miner or mining pool that finds a given block.
Mining Pool
A collection of individual miners who ‘pool’ their efforts or hashing power together and share the block reward. Miners create pools because it increases their chances of earning a block reward.
Learn more about mining pools.
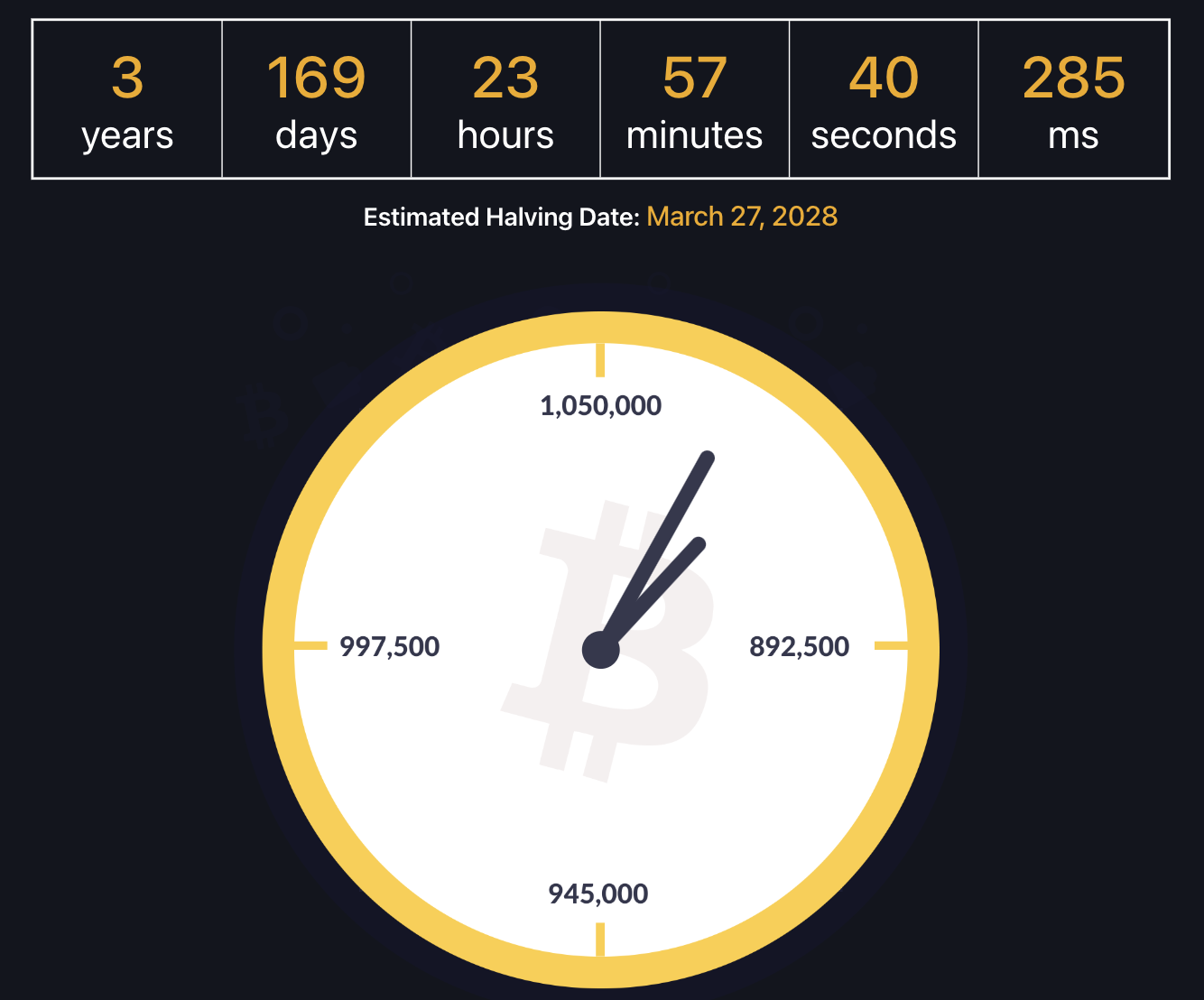
Block Reward Halving
Approximately every 4 years, the block reward gets cut in half. The first block reward ever mined was in 2008 and it it was for 50 Bitcoins. That block reward lasted for four years, where in 2012, the first reward halving occurred and it dropped to 25 Bitcoins.
In 2016, a second halving occurred where the reward was reduced to 12.5 Bitcoins. And as of the time of this writing, we are on the cusp of the third halving (ETA May 11th), where the reward will be cut down to 6.25 Bitcoins. You can find the most up to date estimation of exactly when the next halving will occur on our bitcoin block reward halving clock.
Hashing Power (or Hash Rate)
How many calculations (hashes) a miner can perform per second.
Or it can refer to the total amount of hashing done on a chain by all miners put together - also known as “Net Hash”.
You can learn more about Hash Rate by reading our article about it.
Difficulty
Measured in Trillions, mining difficulty refers to how hard it is to find a block. The current level of difficulty on the Bitcoin blockchain is the primary reason why it is not profitable to mine for most people.
Difficulty Adjustment
Bitcoin was designed to produce block reliably every 10 minutes. Because total hashing power (or Net Hash) is constantly changing, the difficulty of finding a block needs to adjust proportional to the amount of total hashing power on the network.
In very simple terms, if you have four miners on the network, all with equal hashing power, and two stop mining, blocks would happen ever 20 minutes instead of every ten. Therefore, the difficulty of finding blocks also needs to cut in half, so that blocks can continue to be found every 10 minutes.
Difficulty adjustments happen every 2,016 blocks. This should mean that if a new block is added every 10 minutes, then a difficulty adjustment would occur every two weeks. The 10 minute block rule is just a goal though. Some blocks are added after more than 10 minutes. Some are added after less. Its a law of averages and a lot if left up to chance. That doesn’t mean that for the most part, blocks are added reliably every 10 minutes.
Kilowatt Hour
A measurement of energy consumption per hour. Most ASIC miners will tell you how much energy they consume using this metric.
Bonus Chapter 3
Is Bitcoin Mining a Waste of Electricity?
The media constantly says Bitcoin mining is a waste of electricity.
But, there are some problems with their theories as we’ll discuss.
Isn’t Mining a Waste of Electricity?
Certain orthodox economists have criticized mining as wasteful.
It must be kept in mind however that this electricity is expended on useful work:
Enabling a monetary network worth billions (and potentially trillions) of dollars!
Compared to the carbon emissions from just the cars of PayPal’s employees as they commute to work, Bitcoin’s environmental impact is negligible.
As Bitcoin could easily replace PayPal, credit card companies, banks and the bureaucrats who regulate them all, it begs the question:
Isn’t traditional finance a waste?
Not just of electricity, but of money, time and human resources!
Mining Difficulty
If only 21 million Bitcoins will ever be created, why has the issuance of Bitcoin not accelerated with the rising power of mining hardware?
Issuance is regulated by Difficulty, an algorithm which adjusts the difficulty of the Proof of Work problem in accordance with how quickly blocks are solved within a certain time frame (roughly every 2 weeks or 2016 blocks).
Difficulty rises and falls with deployed hashing power to keep the average time between blocks at around 10 minutes.
For most of Bitcoin’s history, the average block time has been about 9.7 minutes. Because the price is always rising, mining power does come onto the network at a fast speed which creates faster blocks. However, for most of 2019 the block time has been around 10 minutes. This is because Bitcoin’s price has remained steady for most of 2019.
Block Reward Halving
Satoshi designed Bitcoin such that the block reward, which miners automatically receive for solving a block, is halved every 210,000 blocks (or roughly 4 years).
As Bitcoin’s price has risen substantially (and is expected to keep rising over time), mining remains a profitable endeavor despite the falling block reward… at least for those miners on the bleeding edge of mining hardware with access to low-cost electricity.
Honest Miner Majority Secures the Network
To successfully attack the Bitcoin network by creating blocks with a falsified transaction record, a dishonest miner would require the majority of mining power so as to maintain the longest chain.
This is known as a 51% attack and it allows an attacker to spend the same coins multiple times and to blockade the transactions of other users at will.
To achieve it, an attacker needs to own mining hardware than all other honest miners.
This imposes a high monetary cost on any such attack.
At this stage of Bitcoin’s development, it’s likely that only major corporations or states would be able to meet this expense… although it’s unclear what net benefit, if any, such actors would gain from degrading or destroying Bitcoin.
Mining Centralization
Pools and specialized hardware has unfortunately led to a centralization trend in Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin developer Greg Maxwell has stated that, to Bitcoin’s likely detriment, a handful of entities control the vast majority of hashing power.
It is also widely-known that at least 50% of mining hardware is located within China.
However, it’s may be argued that it’s contrary to the long-term economic interests of any miner to attempt such an attack.
The resultant fall in Bitcoin’s credibility would dramatically reduce its exchange rate, undermining the value of the miner’s hardware investment and their held coins.
As the community could then decide to reject the dishonest chain and revert to the last honest block, a 51% attack probably offers a poor risk-reward ratio to miners.
Bitcoin mining is certainly not perfect but possible improvements are always being suggested and considered.
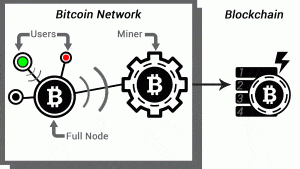
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
This simplified illustration is helpful to explanation:
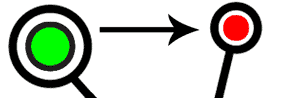
1) Spending
Let’s say the Green user wants to buy some goods from the Red user. Green sends 1 bitcoin to Red.
2) Announcement
Green’s wallet announces a 1 bitcoin payment to Red’s wallet. This information, known as transaction (and sometimes abbreviated as “ tx”) is broadcast to as many Full Nodes as connect with Green’s wallet – typically 8. A full node is a special, transaction-relaying wallet which maintains a current copy of the entire blockchain.

3) Propagation
Full Nodes then check Green’s spend against other pending transactions. If there are no conflicts (e.g. Green didn’t try to cheat by sending the exact same coins to Red and a third user), full nodes broadcast the transaction across the Bitcoin network. At this point, the transaction has not yet entered the Blockchain. Red would be taking a big risk by sending any goods to Green before the transaction is confirmed. So how do transactions get confirmed? This is where Miners enter the picture.
4) Processing by Miners
Miners, like full nodes, maintain a complete copy of the blockchain and monitor the network for newly-announced transactions. Green’s transaction may in fact reach a miner directly, without being relayed through a full node. In either case, a miner then performs work in an attempt to fit all new, valid transactions into the current block.
Miners race each other to complete the work, which is to “package” the current block so that it’s acceptable to the rest of the network. Acceptable blocks include a solution to a Proof of Work(1) computational problem, known as a hash(3). The more computing power a miner controls, the higher their hashrate and the greater their odds of solving the current block.
But why do miners invest in expensive computing hardware and race each other to solve blocks? Because, as a reward for verifying and recording everyone’s transactions, miners receive a substantial Bitcoin reward for every solved block!
And what is a hash? Well, try entering all the characters in the above paragraph, from “But” to “block!” into this hashing utility. If you pasted correctly – as a string hash with no spaces after the exclamation mark – the SHA-256 algorithm used in Bitcoin should produce:
“6afc21238f2d33e24e168195888721dd5ace05d76196671d6739789af92201ed.”
If the characters are altered even slightly, the result won’t match. So, a hash is a way to verify any amount of data is accurate. To solve a block, miners modify non-transaction data in the current block such that their hash result begins with a certain number (according to the current Difficulty, covered below) of zeroes. If you manually modify the string until you get a 0… result, you’ll soon see why this is considered “Proof of Work!”

5) Blockchain Confirmation
The first miner to solve the block containing Green’s payment to Red announces the newly-solved block to the network. If other full nodes agree the block is valid, the new block is added to the blockchain and the entire process begins afresh. Once recorded in the blockchain, Green’s payment goes from pending to confirmed status.
Red may now consider sending the goods to Green. However, the more new blocks are layered atop the one containing Green’s payment, the harder to reverse that transaction becomes. For significant sums of money, it’s recommended to wait for at least 6 confirmations. Given new blocks are produced on average every ten minutes; the wait shouldn’t take much longer than an hour.
The Longest Valid Chain
You may have heard that Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, so why is it advised to await several confirmations? The answer is somewhat complex and requires a solid understanding of the above mining process:
Let’s imagine two miners, A in China and B in Iceland, who solve the current block at roughly the same time. A’s block (A1) propagates through the internet from Beijing, reaching nodes in the East. B’s block (B1) is first to reach nodes in the West. There are now two competing versions of the blockchain!
Which blockchain prevails? Quite simply, the longest valid chain becomes the official version of events. So, let’s say the next miner to solve a block adds it to B’s chain, creating B2. If B2 propagates across the entire network before A2 is found, then B’s chain is the clear winner. A loses his mining reward and fees, which only exist on the invalidated A -chain.
Going back to the example of Green’s payment to Red, let’s say this transaction was included by A but rejected by B, who demands a higher fee than was included by Green. If B’s chain wins then Green’s transaction won’t appear in the B chain – it will be as if the funds never left Green’s wallet.
Although such blockchain splits are rare, they’re a credible risk. The more confirmations have passed, the safer a transaction is considered. This is why what is known as ‘0-conf’ or “0 confirmations” on the Bitcoin Cash blockchain is so dangerous.
Bonus Chapter 4
Frequently Asked Questions
If you’re still a bit confused about what Bitcoin mining is, that’s okay. That’s one reason I built this site, to make it easier to understand!
I’ve curated this FAQ to help to answer any remaining questions.
Can I invest in Bitcoin Miner stocks?
One common question people ask is if they can just invest in the mining companies instead of trying to mine themselves. The answer is: yes, you absolutely can. In fact, there are many publicly traded mining companies, such as Bitmain, Riot, HIVE Blockchain Technologies, Hut8, and BC Group.
And you wouldn't be the only ones investing in these companies. Fidelity, Vanguard, and Charles Schwab Funds have all been buying these stocks en masse.

Big banks are dumping fiat for mining stocks
So when Jamie Dimon, CEO of Chase, denigrates Bitcoin[(4)](#article-sources), just remember that many of his friends at the big banks are loading up on these stocks themselves.
Is Mining With a GPU still profitable?
You can still mine Ethereum and some other coins profitably with GPUs, but when it comes to mining - Bitcoin, No, not even close.
Mining Bitcoins with GPUs has not been profitable since 2016, and even then it was very likely to end up losing you money.
How Will the New US Infrastructure Bill Affect Miners?
The latest infrastructure stimulus bill passed by the Senate in August of 2021 (and awaiting passage in the House) would require that "brokers" of cryptocurrency would be required to report customer information to the Internal Revenue Service. The problem is how broudly "broker" is defined in the law.
"Broker" is any party "responsible for regularly providing any service effectuating transfers of digital assets on behalf of another person".
Using this broad of a definition could mean that software developers, miners, and even everyday citizens simply sending bitcoin to eachother could be considered brokers.
Many (if not most) of these parties have no way of complying with this regulation, and so could not continue business.
That said, how this language is applied is up to the Treasury, which has publicly commented that it would not consider miners and developers or citizens sending bitcoin as "brokers", which is encouraging.

That said, if a regime change occurs at the Treasury Department, this could change, so it is not something miners want to rely on.
For that reason, cryptocurrency interest groups and companies are doing their best to get the clause amended before it can pass in the House of Representatives.
 Chapter 1
Chapter 1
 Chapter 2
Chapter 2
 Chapter 3
Chapter 3
 Chapter 4
Chapter 4
 Chapter 5
Chapter 5
 Chapter 6
Chapter 6